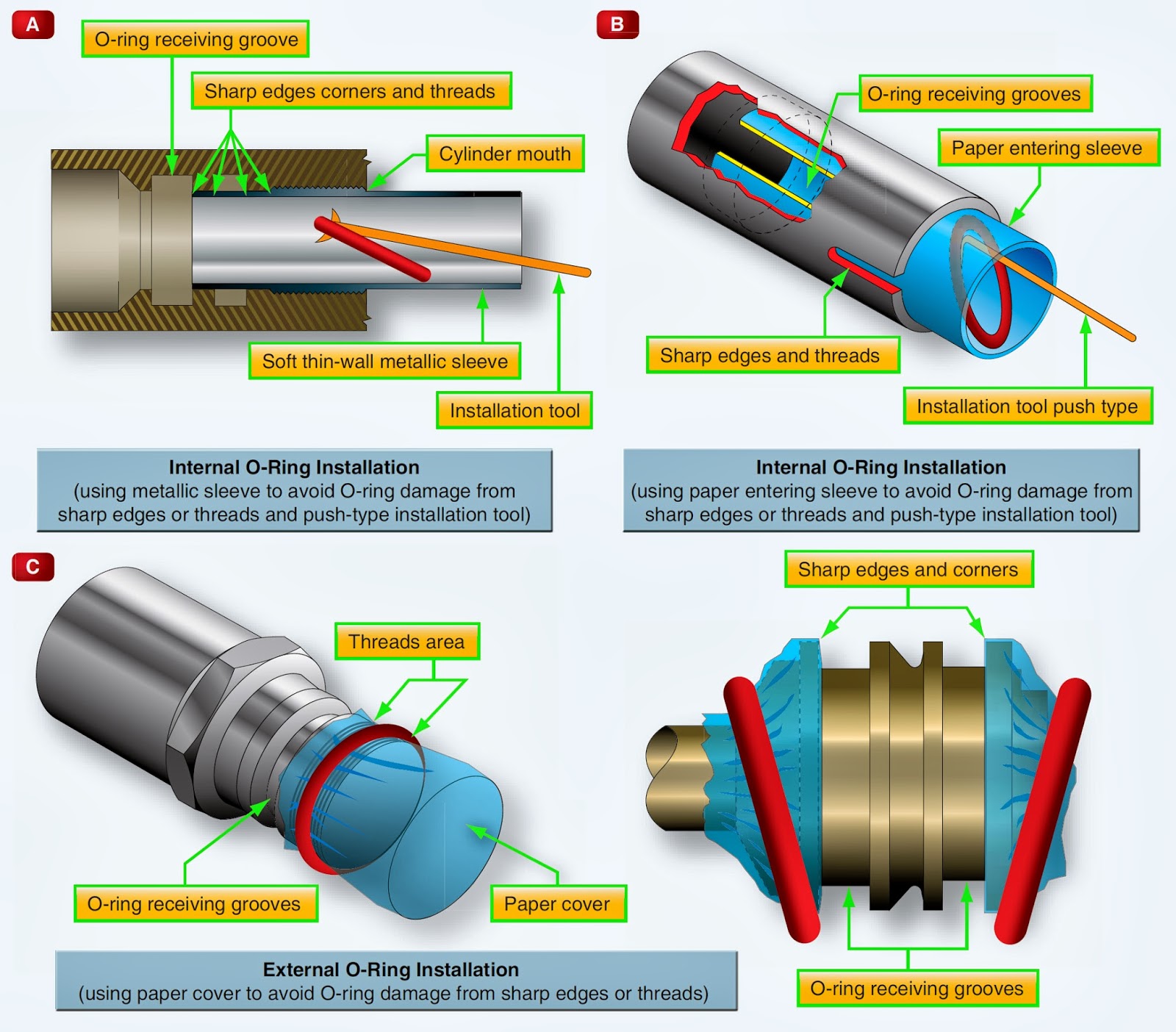
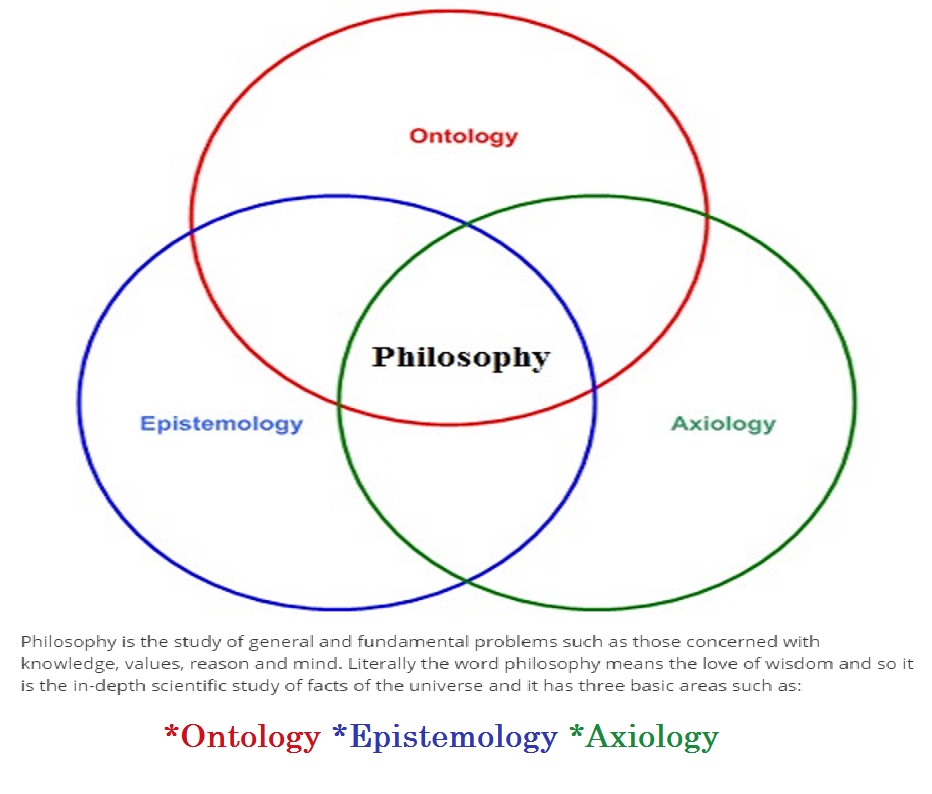
Hartmans contribution is unique in the sense that his Formal Axiology is the only social science in which a onetoone relationship exists between the dimensions of axiology and mathematics. If axiology is viewed as a collective name for aesthetics and ethics, it is similar to value theory. Axiology: The Science of Value The father of modern value science, Robert S. Hartman, observed that we have made our world a paradox where, despite our extraordinary scientific and technological discoveries, we have gained little insight into how to find a sense of inner peace. MEANING OF AXIOLOGY: Axiology is the science of value. The word axiology derived from two Greek words axios means worth or value and logos means logic or theory, means theory of value. The development of the science makes possible the objective measurement of value as accurately as a thermometer measures heat. Axiology studies mainly two kinds of values: ethics and aesthetics. Ethics investigates the concepts of right and good in individual and social conduct. Aesthetics studies the concepts of. Axiology is the science of value. The word Axiology is derived from two Greek roots axios (worth or value) and logos (logic or theory) and so literally it means the theory of value. Only a human person has the status of intrinsic value, or I value; thus, Formal Axiology is a value science with a humanist orientation. Recognizing these three realms of value has enabled Hartman to create a Value Calculus, which provides the tools needed for analysis as precise as chemistry. Axiology as a science is distinguished from axiology as philosophy in three ways: first, in axiology as philosophy the concept of value is a category while in axiology as a science it is the axiom of a system. Axiology, argues the author, provides the basis for ethics as the science of oughtness: the power that a greater good has over a lesser good in compelling our choices. The book concludes with a survey of efforts to establish Axiology as a science. This book expounds the basic principles of Axiology as a major field of philosophical inquiry. Those principles can be discovered and demonstrated by scientific method. In treating scientific inquiry the book throws light on what values are and how they are known. It explores questions of Good and. Axiology: Axiology, (from Greek axios, worthy; logos, science), also called Theory Of Value, the philosophical study of goodness, or value, in the widest sense of these terms. Its significance lies (1) in the considerable expansion that it has given to the meaning of the term value and (2) in the The term value theory is used in at least three different ways in philosophy. In its broadest sense, value theory is a catchall label used to encompass all branches of moral philosophy, social and political philosophy, aesthetics, and sometimes feminist philosophy and the philosophy of. Axiology is both a philosophy and a science of value. Value is how you make an assessment of what is good, invaluable, worth, helpful or moral and what is bad, unvalued unworthy, harmful, or immoral. The science of value, or value science, is a creation of philosopher Robert S. Hartman, which attempts to formally elucidate value theory using both formal and symbolic logic. The fundamental principle, which functions as an axiom, and can be stated in symbolic logic, is. This book expounds the basic principles of Axiology as a major field of philosophical inquiry. Those principles can be discovered and demonstrated by scientific method. A history of axiology: the science of value. The quest for a science of value originated with early Greek philosophers work taking a giant leap forwards when the father of modern value science, Robert S Hartman, developed his value theory, in an attempt to define the meaning of what is good since philosophy had failed to define this. Science: In its original signification as the Latin translation of the Greek term theoria, science referred to the contemplation of the universal principles of order assumed to rule the universe, principles which were treated as superior to and unchangeable by human beings. In its modern signification science refers to the systematic mathematical modeling, for the Axiology, (from Greek axios, worthy; logos, science), also called Theory Of Value, the philosophical study of goodness, orvalue, in the widest sense of these terms. Its significance lies (1) in the considerable expansion that it has given to the meaningof the term value and (2) in the unification that it has provided for the study. Axiology, argues the author, provides the basis for ethics as the science of oughtness: the power that a greater good has over a lesser good in compelling our choices. The book concludes with a survey of efforts to establish Axiology as a science. Axiology is a branch of philosophy that studies judgements about the value. Specifically, axiology is engaged with assessment of the role of researchers own value on all stages of the research process. Axiology primarily refers to the aims of the research. value inquiries, axiology is the most general value science; its primary task is to inquire into the nature of values, that is, of all values, and thus of what all values have in common (p. AxiologyThe Science of Value Misaligned Valuing Habits. After all, this is why the Project Management Institute (PMI) exists. PMI grew from the need for systemic practices. In 1969, five people gathered to pull together the best ideas and practices around project management. Axiology is the study of values. XQ is short for aXiology Quotient. We each have a unique valuing pattern developed over a lifespan of experiences that interacts with our personality and our life choices and ability to make decisions and solve questions. Axiology definition is the study of the nature, types, and criteria of values and of value judgments especially in ethics. the study of the nature, types, and criteria of values and of value judgments especially in ethics With his book, The New Science of Axiological Psychology Leon Pomeroy achieved a very important milestone: He proofed the scientific evidence of the Hartman Value Profile (HVP). Before, only a number of studies about the HVP were available however no structured approach to validate the HVP on a sound scientific basis had been undertaken. Axiology: A Theory of Value ur contemporary age is an age of great confusion and turmoil. W ars able to embrace and even guide science. Ultimately, it must be a value perspective centered on the true love of God. It is precisely s uch a value and value, that. Axiology is the recently adopted term used to cover the philosophy of values. It was introduced a century or so ago by the French philosopher Paul Lapie and derives from the Greek axios, corresponding to the Latin valere, meaning to be strong or to be worthy. Keyword: Axiology, Value education, Teacher education, Curriculum. Today there is a rapid advancement in technology and science is taken place. With the rise in material advancement, we are lacking our cultural and moral standards. Axiology is the science of value. The word 'axiology derived from two Greek roots 'axios' (worth or value) and 'logos' (logic or theory), means the theory of value. The development of the science makes possible the objective measurement of value as accurately as a thermometer measures heat. The word Axiology is from Greek, word axios meaning worthy, and Logos, meaning discourse or study Thus, Axiology is the course or study of the philosophy or system of Value judgments or worthiness. connection with the formal axiology or value theory of Robert S. Articles may be critical, constructive, creative, theoretical, or applied. The Journal of Formal Axiology: Theory and Practice Vol. 6, Summer of 2013 CONTENTS science and value judgment, attempting many times to establish a world center in. Essentially, an assessment based on the science of axiology uncovers the value structure that each person uses to guide their decisionmaking. How Does this Measurement Impact a Hiring Decision? When you put together axios and logos, an assessment based on axiology measures what a person values, the weight placed on those values, and how that. Unification axiology seeks to present such a view of value. This new view of value is presented for the sake of establishing our future society. The future society is a society that will be built by people of original nature, whose intellect, emotion, and will are centered on Heart. Axiology, according to its Greek etymology, means theory of values. The term was introduced at the beginning of the twentieth century when it became a recognized part of philosophy. As a discipline distinct from science, axiology was sometimes even equated with the whole of philosophy, especially in Germany. Simply defined, Axiology is the science of value. The word 'axiology derived from two Greek roots ' axios ' (worth or value) and ' logos ' (logic or theory), means the theory of value. The development of the science makes possible the objective measurement of value as accurately as a. Axiology and Science The search for a science of value originated. with early Greek philosophers in 5 th and 6 th. Only a human person has the status of intrinsic value, or I value; thus, Formal Axiology is a value science with a humanist orientation. Recognizing these three realms of value has enabled Hartman to create a Value Calculus, which provides the tools needed for analysis as precise as chemistry. Axiology, as The science of values by manuelramos View this thread on steemit. Axiology, as The science of values. in principle, are the foundations of the science of formal axiology, as that science which does for value situations and value sciences what mathematics does for natural situations and natural sciences. MORAL VALUE AND AXIOLOGICAL VALUE THE MEASUREMENT OF VALUE. This book expounds the basic principles of Axiology as a major field of philosophical inquiry. Those principles can be discovered and demonstrated by scientific method. In treating scientific inquiry the book throws light on what values are and how they are known. Axiology is the science that studies how people think. Specifically, Axiologists study how people determine the value of different things. This is how individuals compare things and how those value assignments either represent or distort reality. Formal Axiology and the Philosophy of Social Science; esp. , Political Science Introduction In the 22 centuries from Aristotle to Galileo, mans way of life, and knowledge of nature, changed very little compared to the explosion of invention and discovery in the mere four centuries since Galileo. Axiology (from Greek, axia, value, worth; and, logia) is the philosophical study of value. It is either the collective term for ethics and aesthetics [1, philosophical fields that depend crucially on notions of worth, or the foundation for these fields, and thus similar to value theory and metaethics. Formal axiology is the logicbased science of value anchored in a hierarchy of meaning from the most meaningful or richest value to the most destructive or greatest value loss. The logic specifies 18 different levels of richness. Hartman was nominated for a Nobel Prize for his work on the Hartman Value Profile, which is based on the science of axiology. Hartman was born in Berlin on January 27, 1910. Axiology, argues the author, provides the basis for ethics as the science of oughtness: the power that a greater good has over a lesser good in compelling our choices. The book concludes with a survey of efforts to establish Axiology as a science. Understanding Value Science The development of the science makes possible the measurement of value as accurately as a thermometer measures heat. As we have seen the quest for a value science originated with the early Greek philosophers but the acknowledge father of value science is Dr Robert S Hartman. The science of axiology provides a. Axiology is the study of value, i. , what makes good things good and bad things bad 2. Recall that the main point is to determine what. Note: Citations are based on reference standards. However, formatting rules can vary widely between applications and fields of interest or study. The specific requirements or preferences of your reviewing publisher, classroom teacher, institution or organization should be applied..